What is Low-E Glass? Pros & Cons
The low-E glass (Low emissivity) was designed to minimize the amount of infrared and ultraviolet light that comes from the sun and enters through your glass, without losing the amount of light that enters your home.
Low-e glass has a microscopically thin, transparent coating of tiny metal oxide layers that drastically reduces energy transfer and reflects the internal energy back into your room. It can be cold or heat energy. You can experience a consistent indoor temperature, which will provide you with enhanced visual and thermal comfort.
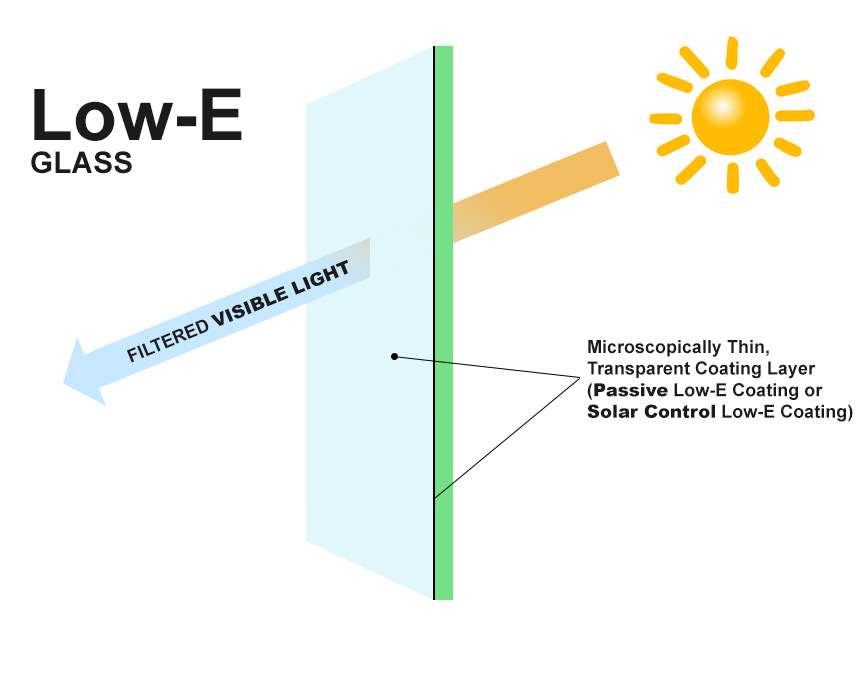
There are 2-Two Types of Low-E Coatings.
– Passive Low-E Coatings (Which is Hard-Coat).
– Solar Control Low-E Coatings (which is Soft-Coat).
Which is Best ?
Passive Low-E coatings
Good for cold locations where the temperature is always (-) minus degrees.
Solar Control Low-E Coating
Good for tropical or where temperature changes according to climate.
Low-E Glass Pros and Cons
Pros:
Make your home more energy-efficient, protect it from UV Rays, Reduce Internal Room Energy Transfer through Door Window Glass.
Cons:
You can have a slightly darker feel because of the layer of glass. Plus, Low-E Coating Glass is expensive.










