Thermal Insulation for Doors & Windows: Ultimate Guide
What is Thermal Insulation in Relation to Doors and Windows?
Thermal insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient environment within buildings. When it comes to doors and windows, thermal insulation refers to their ability to prevent the transfer of heat between the interior and exterior spaces of a structure. This article delves into the significance of thermal insulation in doors and windows, the methods used to achieve it, and the benefits it offers.
The Importance of Thermal Insulation
Thermal insulation is a key factor in regulating indoor temperatures. In regions with varying climate conditions, such as cold winters and hot summers, well-insulated doors and windows help create a barrier that restricts heat exchange. This translates to reduced energy consumption for both heating and cooling systems. As a result, occupants can enjoy a comfortable indoor environment regardless of the weather outside, while simultaneously decreasing their energy bills.
Methods of Achieving Thermal Insulation
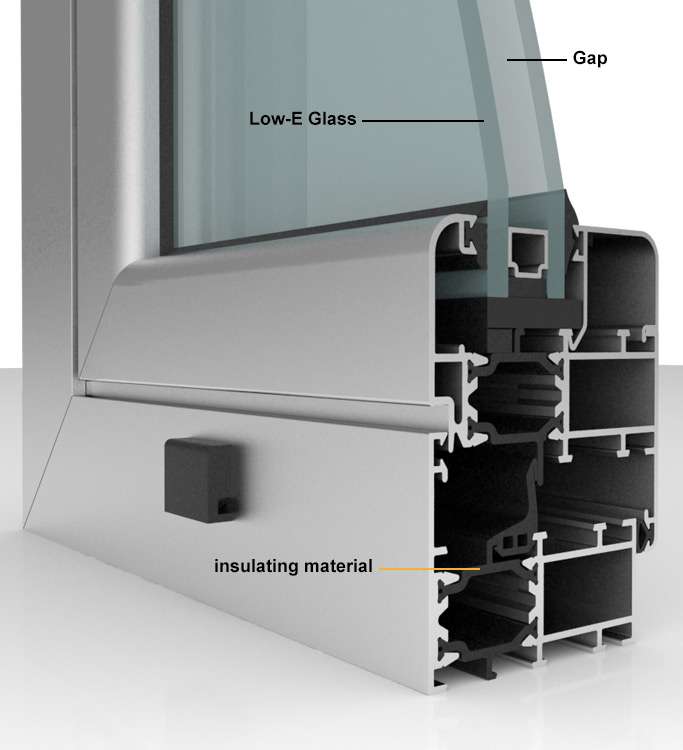
Insulated Glass and Double-Paned Windows: One effective method involves using materials with low thermal conductivity, such as insulated glass or double-paned windows. These windows are designed with a layer of air or gas trapped between the panes, providing an additional insulation barrier. This layer of air or gas acts as a buffer, inhibiting the transfer of heat through the windows.
Weatherstripping and Sealing: Drafts and air leakage can compromise the effectiveness of thermal insulation. Adding weatherstripping or sealing around the edges of doors and windows helps prevent these issues. By closing gaps and minimizing air infiltration, the overall thermal efficiency of the building is enhanced.
Thermal Breaks and Spacers: Thermal breaks or spacers are materials strategically placed between the interior and exterior parts of door and window frames. These materials serve to reduce the transfer of heat, enhancing the insulation properties of the entire structure. By creating separation between the two sides of the frame, thermal bridges are minimized.
Low-Emissivity Coatings: Low-emissivity (low-e) coatings are designed to reflect heat back into the room while preventing its escape through the window. These coatings are applied to the glass surface and help regulate heat transfer. By controlling the passage of radiant heat, they contribute significantly to the overall thermal performance of doors and windows.
Benefits of Enhanced Thermal Insulation

Investing in effective thermal insulation for doors and windows offers several notable benefits:
Energy Savings: Reduced heat exchange through well-insulated doors and windows results in lower energy consumption for heating and cooling systems. This leads to substantial cost savings on utility bills.
Environmental Impact: By decreasing energy consumption, buildings with improved thermal insulation contribute to a lower carbon footprint and reduced greenhouse gas emissions.
Comfort and Livability: Consistent indoor temperatures enhance occupant comfort and create a more pleasant living or working environment. Cutting drafts and cold spots ensures a homogenous and cozy atmosphere.
Noise Reduction: In addition to thermal benefits, many insulation methods also contribute to reducing exterior noise infiltration, promoting a quieter indoor space.
Property Value: Energy-efficient buildings are often more appealing to potential buyers or tenants, increasing the overall value of the property.
Conclusion
Thermal insulation in doors and windows is a critical aspect of maintaining energy efficiency, indoor comfort, and environmental sustainability in buildings. Various methods, such as insulated glass, weatherstripping, thermal breaks, and low-e coatings, contribute to the insulation’s effectiveness. By investing in proper thermal insulation, building owners not only reduce their energy costs but also contribute positively to the environment and provide occupants with a more comfortable living or working environment.
FAQs:
Q: How does thermal insulation affect energy consumption?
A: Thermal insulation reduces heat exchange, leading to decreased energy consumption for heating and cooling systems, ultimately lowering utility bills.
Q: Can I install thermal insulation on existing doors and windows?
A: Yes, retrofitting existing doors and windows with insulation materials or techniques is possible and can improve their energy efficiency.
Q: Are there any government incentives for improving thermal insulation?
A: Many regions offer incentives, rebates, or tax credits to encourage energy-efficient upgrades, including thermal insulation improvements.
Q: Do low-e coatings affect visibility through windows?
A: No, low-e coatings are designed to regulate heat transfer without significantly affecting visibility or clarity through windows.
Q: What other areas of a building can benefit from thermal insulation?
A: Besides doors and windows, roofs, walls, and floors can also benefit from effective thermal insulation to enhance overall energy efficiency and comfort.










